コーデック (Codecs)
✨ 新機能 — [email protected] で導入されました
すべての Zod スキーマは、順方向と逆方向の両方で入力を処理できます:
- 順方向 (Forward):
InputからOutputへ.parse().decode()
- 逆方向 (Backward):
OutputからInputへ.encode()
ほとんどの場合、これは実質的な違いはありません。入力タイプと出力タイプが同一であるため、「順方向」と「逆方向」の間に違いはありません。
しかし、一部のスキーマタイプでは、入力タイプと出力タイプが分岐します。特に z.codec() がそうです。コーデックは、他の2つのスキーマ間の 双方向変換 を定義する特別なタイプのスキーマです。
これらのケースでは、z.decode() と z.encode() はかなり異なる動作をします。
注意 — ここでの方向や用語に特別な意味はありません。A -> B コーデックで エンコード する代わりに、B -> A コーデックで デコード することもできます。「デコード」と「エンコード」という用語の使用は単なる慣習です。
これは、ネットワーク境界でデータを解析する場合に特に便利です。クライアントとサーバー間で単一の Zod スキーマを共有し、この単一のスキーマを使用して、ネットワークに適した形式(例:JSON)と、より豊富な JavaScript 表現との間で変換できます。
コンポーザビリティ (Composability)
注意 — z.encode() と z.decode() はどのスキーマでも使用できます。ZodCodec である必要はありません。
コーデックは他のスキーマと同様にスキーマです。オブジェクト、配列、パイプなどの内部にネストできます。どこで使用できるかについてのルールはありません!
型安全な入力 (Type-safe inputs)
.parse() と .decode() は 実行時 には同じように動作しますが、型シグネチャが異なります。.parse() メソッドは unknown を入力として受け入れ、スキーマの推論された 出力タイプ に一致する値を返します。対照的に、z.decode() と z.encode() 関数は 強く型付けされた入力 を持ちます。
なぜ違いがあるのでしょうか?エンコードとデコードは 変換 を意味します。多くの場合、これらのメソッドへの入力はアプリケーションコードですでに強く型付けされているため、z.decode/z.encode は、コンパイル時に間違いを表面化するために、強く型付けされた入力を受け入れます。
以下は、parse()、decode()、および encode() の型シグネチャの違いを示す図です。
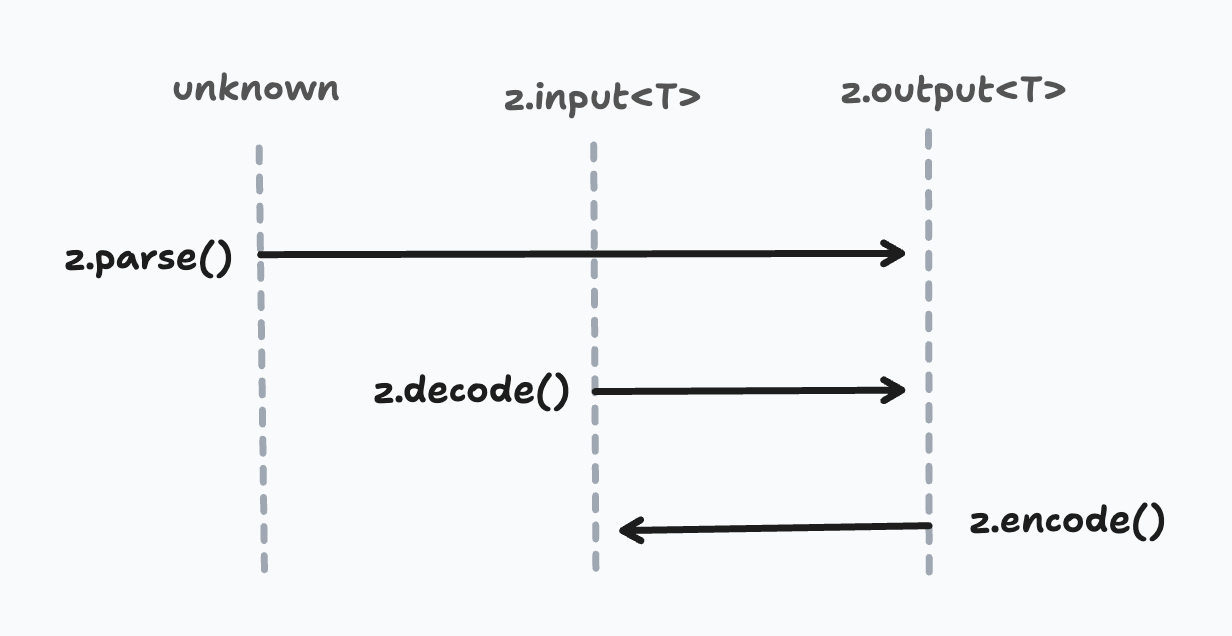
非同期および安全なバリアント (Async and safe variants)
.transform() や .refine() と同様に、コーデックは非同期変換をサポートします。
通常の parse() と同様に、decode() と encode() には「安全 (safe)」および「非同期 (async)」のバリアントがあります。
エンコードの仕組み (How encoding works)
Zod スキーマによっては、解析動作を「反転」させる方法に微妙な点があります。
コーデック (Codecs)
これはかなり自明です。コーデックは、2つのタイプ間の双方向変換をカプセル化します。z.decode() は decode 変換をトリガーして入力を解析された値に変換し、z.encode() は encode 変換をトリガーしてシリアル化して戻します。
パイプ (Pipes)
豆知識 — コーデックは実際には、内部的には「中間」変換ロジックで強化されたパイプの サブクラス として実装されています。
通常のデコード中、ZodPipe<A, B> スキーマは最初に A でデータを解析し、次にそれを B に渡します。ご想像のとおり、エンコード中は、データは最初に B でエンコードされ、次に A に渡されます。
リファインメント (Refinements)
すべてのチェック(.refine()、.min()、.max() など)は、双方向で実行されます。
カスタム .refine() ロジックでの予期しないエラーを回避するために、Zod は z.encode() 中に2つの「パス」を実行します。最初のパスでは、入力タイプが期待されるタイプに準拠していることを確認します(invalid_type エラーなし)。それが合格した場合、Zod はリファインメントロジックを実行する2番目のパスを実行します。
このアプローチは、z.string().trim() や z.string().toLowerCase() のような「変異変換」もサポートします。
デフォルトとプリフォールト (Defaults and prefaults)
デフォルトとプリフォールトは、「順方向」にのみ適用されます。
スキーマにデフォルト値をアタッチすると、入力はオプション (| undefined) になりますが、出力はそうなりません。したがって、undefined は z.encode() への有効な入力ではなく、デフォルト/プリフォールトは適用されません。
キャッチ (Catch)
同様に、.catch() は「順方向」にのみ適用されます。
Stringbool
注意 — Stringbool は、Zod にコーデックが導入される前から存在していました。それ以来、内部的にコーデックとして再実装されました。
z.stringbool() API は、文字列値 ("true", "false", "yes", "no" など) を boolean に変換します。デフォルトでは、z.encode() 中に true を "true" に、false を "false" に変換します。
カスタムの truthy と falsy 値のセットを指定した場合、配列の最初の要素 が代わりに使用されます。
変換 (Transforms)
⚠️ — .transform() API は、一方向 変換を実装します。スキーマ内のどこかに .transform() が存在する場合、z.encode() 操作を試行すると 実行時エラー がスローされます(ZodError ではありません)。
便利なコーデック (Useful codecs)
以下は、一般的に必要とされる多くのコーデックの実装です。カスタマイズ性のために、これらは Zod 自体のファーストクラス API としては含まれていません。代わりに、それらをプロジェクトにコピー/貼り付けし、必要に応じて変更してください。
注意 — これらのコーデック実装はすべて、正確性がテストされています。
stringToNumber
parseFloat() を使用して、数値の文字列表現を JavaScript の number 型に変換します。
stringToInt
parseInt() を使用して、整数の文字列表現を JavaScript の number 型に変換します。
stringToBigInt
文字列表現を JavaScript の bigint 型に変換します。
numberToBigInt
JavaScript の number を bigint 型に変換します。
isoDatetimeToDate
ISO 日時文字列を JavaScript の Date オブジェクトに変換します。
epochSecondsToDate
Unix タイムスタンプ(エポックからの秒数)を JavaScript の Date オブジェクトに変換します。
epochMillisToDate
Unix タイムスタンプ(エポックからのミリ秒数)を JavaScript の Date オブジェクトに変換します。
json(schema)
JSON 文字列を構造化データに解析し、JSON にシリアル化して戻します。この汎用関数は、解析された JSON データを検証するための出力スキーマを受け入れます。
特定のスキーマを使用した使用例:
utf8ToBytes
UTF-8 文字列を Uint8Array バイト配列に変換します。
bytesToUtf8
Uint8Array バイト配列を UTF-8 文字列に変換します。
base64ToBytes
base64 文字列を Uint8Array バイト配列に変換します(その逆も同様)。
base64urlToBytes
base64url 文字列 (URL セーフな base64) を Uint8Array バイト配列に変換します。
hexToBytes
16進文字列を Uint8Array バイト配列に変換します(その逆も同様)。
stringToURL
URL 文字列を JavaScript の URL オブジェクトに変換します。
stringToHttpURL
HTTP/HTTPS URL 文字列を JavaScript の URL オブジェクトに変換します。
uriComponent
encodeURIComponent() と decodeURIComponent() を使用して URI コンポーネントをエンコードおよびデコードします。

