編解碼器 (Codecs)
✨ 新功能 — 在 [email protected] 中引入
所有 Zod 架構都可以按前向和後向兩個方向處理輸入:
- 前向 (Forward):
Input到Output.parse().decode()
- 後向 (Backward):
Output到Input.encode()
在大多數情況下,這只是名稱上的區別而沒有實際差異。輸入和輸出類型是相同的,因此「前向」和「後向」沒有區別。
然而,某些架構類型會導致輸入和輸出類型發生分歧,尤其是 z.codec()。編解碼器是一種特殊類型的架構,它定義了另外兩個架構之間的 雙向轉換。
在這些情況下,z.decode() 和 z.encode() 的行為截然不同。
注意 — 這裡的方向或術語沒有什麼特別的。你可以用 B -> A 編解碼器進行 解碼,而不是用 A -> B 編解碼器進行 編碼。「解碼」和「編碼」這些術語的使用只是一種約定。
這在解析網絡邊界處的數據時特別有用。您可以在客戶端和服務器之間共享單個 Zod 架構,然後使用這單個架構在網絡友好格式(例如 JSON)和更豐富的 JavaScript 表示之間進行轉換。
可組合性 (Composability)
注意 — 您可以將 z.encode() 和 z.decode() 用於任何架構。它不必是 ZodCodec。
編解碼器像其他任何架構一樣。您可以將它們嵌套在對象、數組、管道等內部。對於在哪裡可以使用它們沒有規則!
類型安全輸入 (Type-safe inputs)
雖然 .parse() 和 .decode() 在 運行時 表現相同,但它們具有不同的類型簽名。.parse() 方法接受 unknown 作為輸入,並返回與架構推斷的 輸出類型 匹配的值。相比之下,z.decode() 和 z.encode() 函數具有 強類型輸入。
為什麼會有差異?編碼和解碼意味著 轉換。在許多情況下,這些方法的輸入在應用程序代碼中已經是強類型的,因此 z.decode/z.encode 接受強類型輸入以在編譯時顯示錯誤。
這是一張演示 parse()、decode() 和 encode() 的類型簽名之間差異的圖表。
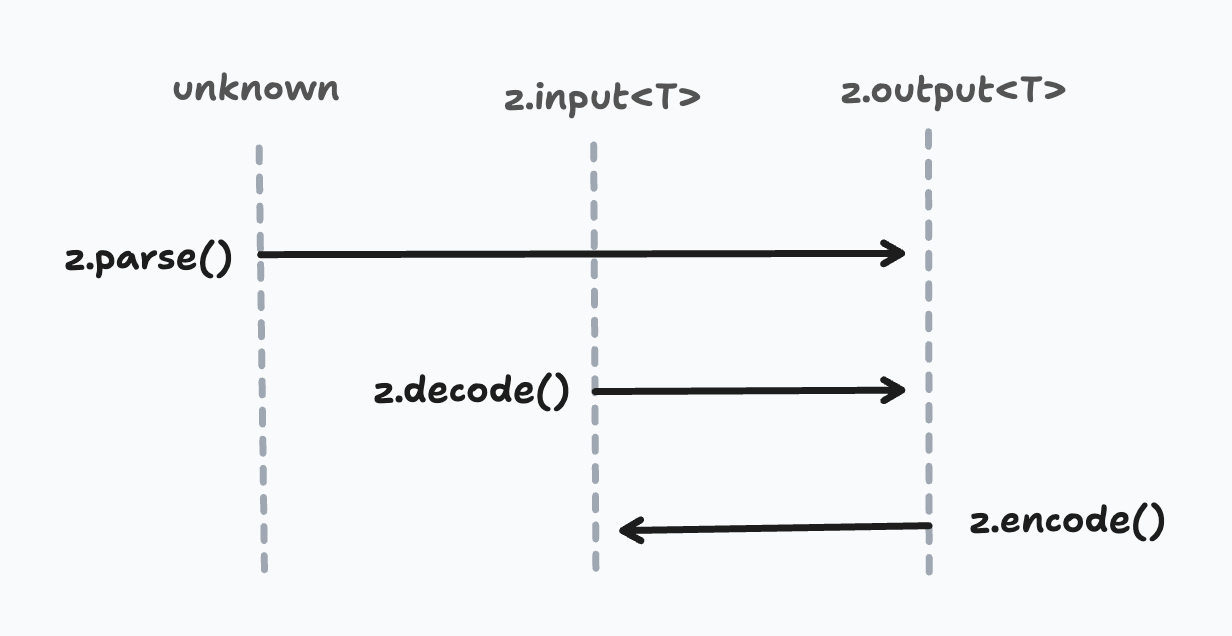
異步和安全變體 (Async and safe variants)
與 .transform() 和 .refine() 一樣,編解碼器支持異步轉換。
與常規 parse() 一樣,decode() 和 encode() 也有「安全」和「異步」變體。
編碼的工作原理 (How encoding works)
某些 Zod 架構如何「反轉」其解析行為存在一些細微差別。
編解碼器 (Codecs)
這一點不言自明。編解碼器封裝了兩種類型之間的雙向轉換。z.decode() 觸發 decode 轉換以將輸入轉換為解析值,而 z.encode() 觸發 encode 轉換以將其序列化回來。
管道 (Pipes)
有趣的事實 — 編解碼器實際上在內部實現為管道的 子類,並增加了「間隙」轉換邏輯。
在常規解碼期間,ZodPipe<A, B> 架構將首先用 A 解析數據,然後將其傳遞給 B。正如您所料,在編碼期間,數據首先用 B 編碼,然後傳遞給 A。
細化 (Refinements)
所有檢查(.refine()、.min()、.max() 等)仍然在兩個方向上執行。
為了避免自定義 .refine() 邏輯中出現意外錯誤,Zod 在 z.encode() 期間執行兩次「傳遞」。第一次傳遞確保輸入類型符合預期類型(沒有 invalid_type 錯誤)。如果該傳遞通過,Zod 將執行第二次傳遞,該傳遞執行細化邏輯。
這種方法還支持「變異轉換」,如 z.string().trim() 或 z.string().toLowerCase():
默認值和預設值 (Defaults and prefaults)
默認值和預設值僅在「前向」方向應用。
當您將默認值附加到架構時,輸入變為可選的 (| undefined),但輸出不是。因此,undefined 不是 z.encode() 的有效輸入,並且不會應用默認值/預設值。
捕獲 (Catch)
同樣,.catch() 僅在「前向」方向應用。
Stringbool
注意 — Stringbool 早於 Zod 中編解碼器的引入。它後來在內部重新實現為編解碼器。
z.stringbool() API 將字串值("true"、"false"、"yes"、"no" 等)轉換為 boolean。默認情況下,它將在 z.encode() 期間將 true 轉換為 "true",將 false 轉換為 "false"。
如果您指定一組自定義的 truthy(真值)和 falsy(假值)值,則將使用 數組中的第一個元素。
轉換 (Transforms)
⚠️ — .transform() API 實現了 單向 轉換。如果在您的架構中任何地方存在 .transform(),嘗試 z.encode() 操作將拋出 運行時錯誤(而不是 ZodError)。
有用的編解碼器 (Useful codecs)
以下是一些常用編解碼器的實現。為了可定製性,這些未作為一等 API 包含在 Zod 本身中。相反,您應該將它們複製/粘貼到您的項目中並根據需要進行修改。
注意 — 所有這些編解碼器實現都已通過正確性測試。
stringToNumber
使用 parseFloat() 將數字的字串表示形式轉換為 JavaScript number 類型。
stringToInt
使用 parseInt() 將整數的字串表示形式轉換為 JavaScript number 類型。
stringToBigInt
將字串表示形式轉換為 JavaScript bigint 類型。
numberToBigInt
將 JavaScript number 轉換為 bigint 類型。
isoDatetimeToDate
將 ISO 日期時間字串轉換為 JavaScript Date 對象。
epochSecondsToDate
將 Unix 時間戳(自紀元以來的秒數)轉換為 JavaScript Date 對象。
epochMillisToDate
將 Unix 時間戳(自紀元以來的毫秒數)轉換為 JavaScript Date 對象。
json(schema)
將 JSON 字串解析為結構化數據並序列化回 JSON。此泛型函數接受一個輸出架構來驗證解析後的 JSON 數據。
特定架構的使用示例:
utf8ToBytes
將 UTF-8 字串轉換為 Uint8Array 字節數組。
bytesToUtf8
將 Uint8Array 字節數組轉換為 UTF-8 字串。
base64ToBytes
將 base64 字串轉換為 Uint8Array 字節數組,反之亦然。
base64urlToBytes
將 base64url 字串(URL 安全的 base64)轉換為 Uint8Array 字節數組。
hexToBytes
將十六進制字串轉換為 Uint8Array 字節數組,反之亦然。
stringToURL
將 URL 字串轉換為 JavaScript URL 對象。
stringToHttpURL
將 HTTP/HTTPS URL 字串轉換為 JavaScript URL 對象。
uriComponent
使用 encodeURIComponent() 和 decodeURIComponent() 對 URI 組件進行編碼和解碼。

